Data Structure Sparse Array
A sparse array is one in which the elements do not have contiguous indexes starting at 0
前言
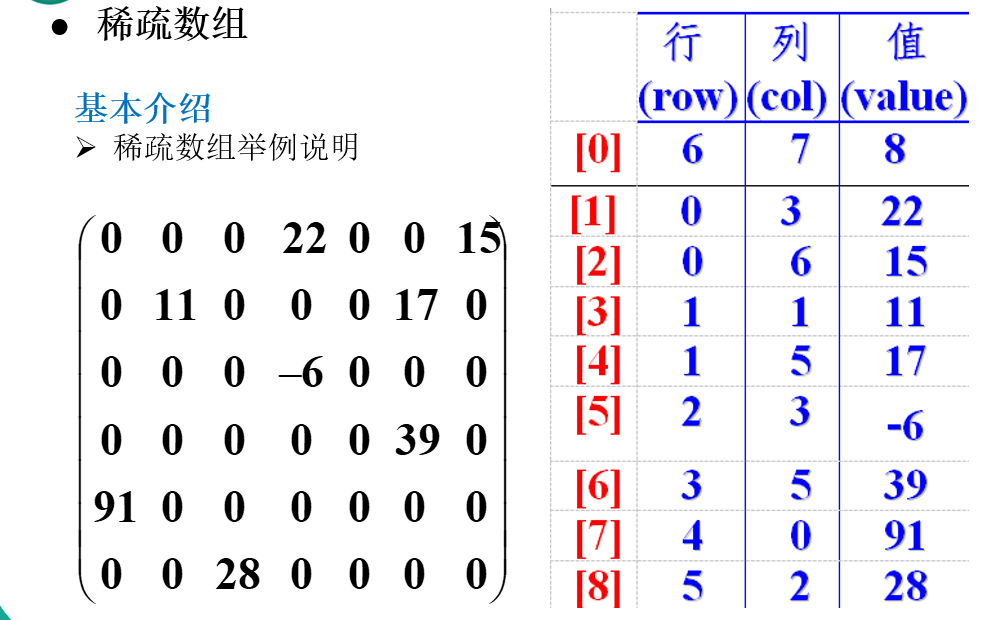
稀疏数组可以看做是普通数组的压缩,但是这里说的普通数组是值无效数据量远大于有效数据量的数组。
问题
当一个数组中大部分元素为0,或者为同一个值的数组时,可以使用稀疏数组来保存该数组。
稀疏数组的处理方法是:
1)记录数组一共有几行几列,有多少个不同的值;
2)把具有不同值的元素的行列及值记录在一个小规模的数组中,从而缩小程序的规模。
解决
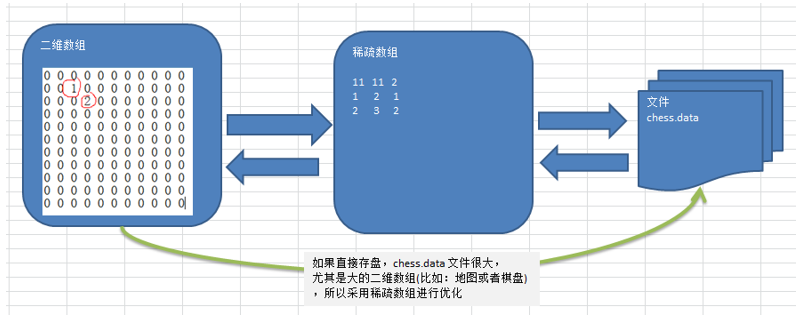
使用稀疏数组,来保留类似前面的二维数组(棋盘、地图等等) 把稀疏数组存盘,并且可以从新恢复原来的二维数组数
整体思路分析:
代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
|
public class SparseArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] chess = new int[11][11];
chess[1][2] = 1;
chess[2][3] = 2;
chess[3][4] = 1;
System.out.println("棋盘原始数据");
printChess(chess);
int[][] sparseArray = toSparseArray(chess);
System.out.println("处理后稀疏数组数据");
printChess(sparseArray);
System.out.println("稀疏数组还原为棋盘原始数据");
int[][] sparseArraytoChess = sparseArraytoChess(sparseArray);
printChess(sparseArraytoChess);
String sparseArrayPath = saveSparseArrayToFile(sparseArray);
System.out.println(sparseArrayPath);
int[][] readSparseArrayFile = readSparseArrayFile(sparseArrayPath);
System.out.println("打印本地读取的稀疏数组数据");
printChess(readSparseArrayFile);
System.out.println("打印本地读取的稀疏数组转换为原始棋盘");
int[][] sparseFileToChess = sparseArraytoChess(readSparseArrayFile);
printChess(sparseFileToChess);
}
private static int[][] readSparseArrayFile(String sparseArrayPath) {
File sourceFile = new File(sparseArrayPath);
int[][] sparseArray = null;
try {
BufferedReader inCount = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(sourceFile));
String line = "";
int count = 1;
while ((line = inCount.readLine()) != null) {
count++;
}
sparseArray = new int[count][3];
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(sourceFile));
int row = 0;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
String[] temp = line.split("\t");
for (int j = 0; j < temp.length; j++) {
sparseArray[row][j] = Integer.parseInt(temp[j]);
}
row++;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return sparseArray;
}
private static String saveSparseArrayToFile(int[][] sparseArray) {
if (sparseArray == null) {
return null;
}
FileWriter fw = null;
File destFile = new File("C:/Users/funin/Documents/temp/map.data");
try {
if (!destFile.exists()) {
destFile.createNewFile();
}
fw = new FileWriter(destFile);
for (int i = 0; i < sparseArray.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < sparseArray[i].length; j++) {
fw.write(sparseArray[i][j] + "\t");
}
fw.write("\r\n");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fw != null) {
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return destFile.getAbsolutePath();
}
private static int[][] sparseArraytoChess(int[][] sparseArray) {
int row = sparseArray[0][0];
int clo = sparseArray[0][1];
int val = sparseArray[0][2];
int[][] chess = new int[row][clo];
for (int j = 1; j <= val; j++) {
int chessRow = sparseArray[j][0];
int chessClo = sparseArray[j][1];
int chessVal = sparseArray[j][2];
chess[chessRow][chessClo] = chessVal;
}
return chess;
}
private static int[][] toSparseArray(int[][] chess) {
int sparseArrayLenth = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < chess.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < chess[i].length; j++) {
if (chess[i][j] != 0) {
sparseArrayLenth++;
}
}
}
int[][] sparseArray = new int[sparseArrayLenth][3];
int count = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < chess.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < chess[i].length; j++) {
if (chess[i][j] != 0) {
sparseArray[count][0] = i;
sparseArray[count][1] = j;
sparseArray[count][2] = chess[i][j];
count++;
}
}
}
sparseArray[0][0] = chess.length;
sparseArray[0][1] = chess.length;
sparseArray[0][2] = count - 1;
return sparseArray;
}
private static void printChess(int[][] chess) {
for (int i = 0; i < chess.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < chess[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(chess[i][j] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
|
延伸
稀疏矩阵
数组 - 稀疏数组
韩顺平数据结构和算法

