High performance scalable web applications often use a distributed in-memory data cache in front of or in place of robust persistent storage for some tasks. In Java Applications it is very common to use in Memory Cache for better performance.
前言 一、 JSR107 Java Caching定义了5个核心接口
CachingProvider
定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个CacheManager。一个应用可以在运行期访问多个CachingProvider。
CacheManager
定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,这些Cache存在于CacheManager的上下文中。一个CacheManager仅被一个CachingProvider所拥有。
Cache
一个类似Map 的数据结构并临时存储以Key为索引 的值。一个Cache仅被一个
Entry
一个存储在Cache中的key-value对。
Expiry
每一个存储在Cache中的条目有一个定义的有效期。一旦超过这个时间,条目为过期的状态。一旦过期,条目将不可访问、更新和删除。缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置。
jsr107示意图:
使用JSR107需要导入如下包
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > javax.cache</groupId > <artifactId > cache-api</artifactId > </dependency >
对于一些cache框架或产品,我们可以发现一些明显不足。
基于以上的一些不足,大杀器缓存框架JetCache出现,基于已有缓存的成熟产品,解决了上面产品的缺陷。主要表现在
二、 Spring缓存抽象 Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache统一 不同的缓存技术;并支持使用JCache(JSR-107) 注解简化我们开发;
Cache接口有以下功能:
为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合;
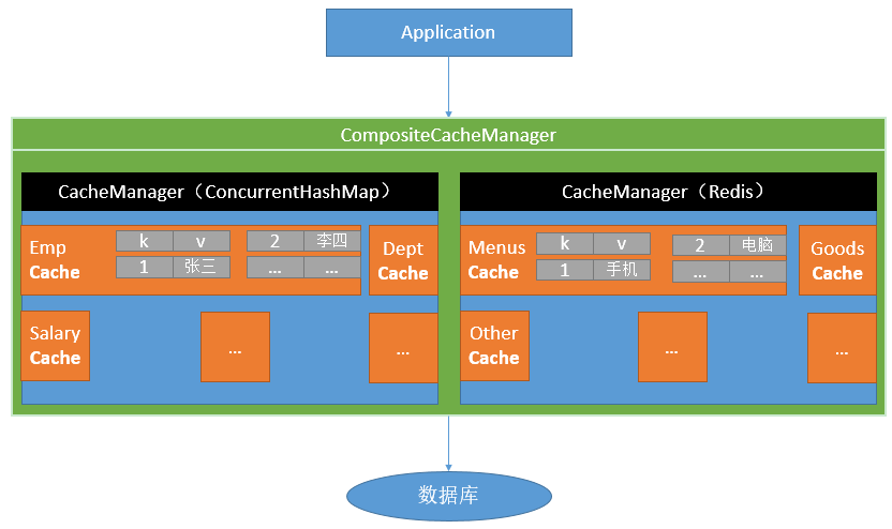
Spring缓存抽象:
三、 重要缓存注解及概念
Cache 缓存接口,定义缓存操作。实现有:RedisCache、EhCacheCache、ConcurrentMapCache等
CacheManager 缓存管理器,管理各种缓存(Cache)组件
@Cacheable 根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存
@CacheEvict 清空缓存
@CachePut 更新缓存
@EnableCaching 开启基于注解的缓存
keyGenerator 缓存数据时key生成策略
serialize 缓存数据时value序列化策略
1 . @Cacheable/@CachePut/@CacheEvict 主要的参数 value
缓存名称,字符串/字符数组形式;
如@Cacheable(value=”mycache”) 或者@Cacheable(value={”cache1”,”cache2”}
key
缓存的key,需要按照SpEL表达式编写,如果不指定则按照方法所有参数进行组合;
如@Cacheable(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName”)
keyGenerator
key的生成器;可以自己指定key的生成器的组件id
注意:key/keyGenerator:二选一使用;
condition
缓存条件,使用SpEL编写,在调用方法之前之后都能判断;
如@Cacheable(value=”testcache”,condition=”#userName.length()>2”)
unless (@CachePut、@Cacheable)
用于否决缓存的条件,只在方法执行之后判断;
如@Cacheable(value=”testcache”,unless=”#result ==null”)
beforeInvocation (@CacheEvict)
是否在执行前清空缓存,默认为false,false情况下方法执行异常则不会清空;
如@CachEvict(value=”testcache”,beforeInvocation=true)
allEntries (@CacheEvict)
是否清空所有缓存内容,默认为false;
如@CachEvict(value=”testcache”,allEntries=true)
2 . 缓存可用的SpEL表达式 root
表示根对象,不可省略
被调用方法名 methodName
如 #root.methodName
被调用方法 method
如 #root.method.name
目标对象 target
如 #root.target
被调用的目标对象类 targetClass
如 #root.targetClass
被调用的方法的参数列表 args
如 #root.args[0]
方法调用使用的缓存列表 caches
如 #root.caches[0].name
参数名
方法参数的名字. 可以直接 #参数名 ,也可以使用 #p0或#a0 的形式,0代表参数的索引;
如 #iban 、 #a0 、 #p0
返回值
方法执行后的返回值(仅当方法执行之后的判断有效,如‘unless’ , @CachePut、@CacheEvict’的表达式beforeInvocation=false )
如 #result
四、 缓存使用 1. 基本使用步骤
引入spring-boot-starter-cache模块
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId > </dependency >
@EnableCaching开启缓存
在主配置类上标注
使用缓存注解
如@Cacheable、@CachePut
切换为其他缓存
2. 搭建实验环境
导入数据库文件 创建出department和employee表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `department` ;CREATE TABLE `department` ( `id` int (11 ) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `departmentName` varchar (255 ) DEFAULT NULL , PRIMARY KEY (`id` ) ) ENGINE =InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET =utf8; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `employee` ;CREATE TABLE `employee` ( `id` int (11 ) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `lastName` varchar (255 ) DEFAULT NULL , `email` varchar (255 ) DEFAULT NULL , `gender` int (2 ) DEFAULT NULL , `d_id` int (11 ) DEFAULT NULL , PRIMARY KEY (`id` ) ) ENGINE =InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET =utf8;
创建javaBean封装数据
整合MyBatis操作数据库
配置数据源信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 spring.datasource.username =root spring.datasource.password =123 spring.datasource.url =jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?serverTimezone=GMT spring.datasource.driver-class-name =com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case =true logging.level.cn.edu.ustc.springboot.mapper =debug debug =true
使用注解版的MyBatis;
@MapperScan指定需要扫描的mapper接口所在的包
主配置类开启@EnableCaching
3. 快速体验缓存 @Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict的使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 @Service public class EmployeeService @Autowired private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper; @Cacheable (value={"emp" }, key = "#id+#root.methodName+#root.caches[0].name" , condition = "#a0>1" , unless = "#p0==2" ) public Employee getEmpById (Integer id) System.out.println("查询员工:" +id); return employeeMapper.getEmpById(id); } @CachePut (value = {"emp" },key = "#employee.id" ) public Employee updateEmp (Employee employee) System.out.println("更新员工" +employee); employeeMapper.updateEmp(employee); return employee; } @CacheEvict (value = {"emp" },allEntries = true ,beforeInvocation = true ) public Integer delEmp (Integer id) int i=1 /0 ; System.out.println("删除员工:" +id); employeeMapper.delEmp(id); return id; } }
自定义KeyGenerator
使用时在注解属性内指定KeyGenerator=“myKeyGenerator”
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Configuration public class MyCacheConfig @Bean ("myKeyGenerator" ) public KeyGenerator myKeyGenerator () return new KeyGenerator(){ @Override public Object generate (Object target, Method method, Object... params) return method.getName()+"[" + Arrays.asList(params).toString()+target+"]" ; } }; } }
@CacheConfig
标注在类上,用于抽取@Cacheable的公共属性
由于一个类中可能会使用多次@Cacheable等注解,所以各项属性可以抽取到@CacheConfig
@Caching
组合使用@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Caching ( cacheable = { @Cacheable (key = "#lastName" ) }, put = { @CachePut (key = "#result.id" ), @CachePut (key = "#result.email" ) } ) public Employee getEmpByLastName (String lastName) return employeeMapper.getEmpByLastName(lastName); }
4. 工作原理 缓存的自动配置类CacheAutoConfiguration向容器中导入了CacheConfigurationImportSelector,此类的selectImports()方法添加了许多配置类,其中SimpleCacheConfiguration默认生效
GenericCacheConfiguration
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @Import ({ CacheConfigurationImportSelector.class , CacheManagerEntityManagerFactoryDependsOnPostProcessor .class }) public class CacheAutoConfiguration static class CacheConfigurationImportSelector implements ImportSelector @Override public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) { CacheType[] types = CacheType.values(); String[] imports = new String[types.length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < types.length; i++) { imports[i] = CacheConfigurations.getConfigurationClass(types[i]); } return imports; } } }
SimpleCacheConfiguration向容器中导入了ConcurrentMapCacheManager
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 @Configuration (proxyBeanMethods = false )@ConditionalOnMissingBean (CacheManager.class ) @Conditional (CacheCondition .class ) class SimpleCacheConfiguration @Bean ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager (CacheProperties cacheProperties, CacheManagerCustomizers cacheManagerCustomizers) ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager = new ConcurrentMapCacheManager(); List<String> cacheNames = cacheProperties.getCacheNames(); if (!cacheNames.isEmpty()) { cacheManager.setCacheNames(cacheNames); } return cacheManagerCustomizers.customize(cacheManager); } }
ConcurrentMapCacheManager使用ConcurrentMap以k-v的方式存储缓存缓存,下面以@Cacheable的运行流程为例说明ConcurrentMapCacheManager的作用。
==@Cacheable的运行流程==
方法运行之前,先去查询Cache(缓存组件),按照cacheNames指定的名字获取 ;
去Cache中查找缓存的内容,使用一个key,默认就是方法的参数;key是按照某种策略生成的 ;默认是使用keyGenerator生成的,默认使用SimpleKeyGenerator生成key;
SimpleKeyGenerator生成key的默认策略;
如果没有参数;key=new SimpleKey();
没有查到缓存就调用目标方法;
将目标方法返回的结果,放进缓存中
@Cacheable标注的方法执行之前先来检查缓存中有没有这个数据,默认按照参数的值作为key去查询缓存,
核心:
源码分析
默认使用ConcurrentMapCacheManager管理缓存,该类使用ConcurrentMap保存缓存,获取缓存如果没有Cache组件会自动创建,并以cacheNames-cache对放入ConcurrentMap。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public class ConcurrentMapCacheManager implements CacheManager , BeanClassLoaderAware private final ConcurrentMap<String, Cache> cacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); private boolean dynamic = true ; public Cache getCache (String name) Cache cache = this .cacheMap.get(name); if (cache == null && this .dynamic) { synchronized (this .cacheMap) { cache = this .cacheMap.get(name); if (cache == null ) { cache = createConcurrentMapCache(name); this .cacheMap.put(name, cache); } } } return cache; } }
在@Cacheable标注方法执行前执行CacheAspectSupport的execute()方法,在该方法中会以一定的规则生成key,并尝试在缓存中通过该key获取值,若通过key获取到值则直接返回,不用执行@Cacheable标注方法,否则执行该方法获得返回值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 public abstract class CacheAspectSupport extends AbstractCacheInvoker implements BeanFactoryAware , InitializingBean , SmartInitializingSingleton { @Nullable private Object execute (final CacheOperationInvoker invoker, Method method, CacheOperationContexts contexts) if (contexts.isSynchronized()) { CacheOperationContext context = contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class ).iterator ().next () ; if (isConditionPassing(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT)) { Object key = generateKey(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT); Cache cache = context.getCaches().iterator().next(); try { return wrapCacheValue(method, cache.get(key, () -> unwrapReturnValue(invokeOperation(invoker)))); } catch (Cache.ValueRetrievalException ex) { throw (CacheOperationInvoker.ThrowableWrapper) ex.getCause(); } } else { return invokeOperation(invoker); } } processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class ), true , CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator .NO_RESULT ) ; Cache.ValueWrapper cacheHit = findCachedItem(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class )) ; List<CachePutRequest> cachePutRequests = new LinkedList<>(); if (cacheHit == null ) { collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class ), CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator .NO_RESULT , cachePutRequests ) ; } Object cacheValue; Object returnValue; if (cacheHit != null && !hasCachePut(contexts)) { cacheValue = cacheHit.get(); returnValue = wrapCacheValue(method, cacheValue); } else { returnValue = invokeOperation(invoker); cacheValue = unwrapReturnValue(returnValue); } collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CachePutOperation.class ), cacheValue , cachePutRequests ) ; for (CachePutRequest cachePutRequest : cachePutRequests) { cachePutRequest.apply(cacheValue); } processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class ), false , cacheValue ) ; return returnValue; } @Nullable private Cache.ValueWrapper findCachedItem (Collection<CacheOperationContext> contexts) { Object result = CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT; for (CacheOperationContext context : contexts) { if (isConditionPassing(context, result)) { Object key = generateKey(context, result); Cache.ValueWrapper cached = findInCaches(context, key); if (cached != null ) { return cached; } else { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No cache entry for key '" + key + "' in cache(s) " + context.getCacheNames()); } } } } return null ; } @Nullable protected Object generateKey (@Nullable Object result) if (StringUtils.hasText(this .metadata.operation.getKey())) { EvaluationContext evaluationContext = createEvaluationContext(result); return evaluator.key(this .metadata.operation.getKey(), this .metadata.methodKey, evaluationContext); } return this .metadata.keyGenerator.generate(this .target, this .metadata.method, this .args); }
默认情况下使用SimpleKeyGenerator生成key
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class SimpleKeyGenerator implements KeyGenerator public static Object generateKey (Object... params) if (params.length == 0 ) { return SimpleKey.EMPTY; } if (params.length == 1 ) { Object param = params[0 ]; if (param != null && !param.getClass().isArray()) { return param; } } return new SimpleKey(params); } }
默认的缓存类ConcurrentMapCache,使用ConcurrentMap存储k-v
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class ConcurrentMapCache extends AbstractValueAdaptingCache private final String name; private final ConcurrentMap<Object, Object> store; protected Object lookup (Object key) return this .store.get(key); } public void put (Object key, @Nullable Object value) this .store.put(key, toStoreValue(value)); } }
五、Redis与缓存 1. 环境搭建 导入依赖
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId > </dependency >
在spring.properties指定Redis服务器地址
1 2 spring.redis.host =192.168.31.162
2. RedisTemplate RedisAutoConfiguration向容器中导入了两个类RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate和StringRedisTemplate,作为Redis客户端分别操作k-v都为对象和k-v都为字符串的值
Redis常见的五大数据类型
String(字符串)、List(列表)、Set(集合)、Hash(散列)、ZSet(有序集合)
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue()[String(字符串)]
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList()[List(列表)]
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet()[Set(集合)]
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash()[Hash(散列)]
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet()[ZSet(有序集合)]
3. Redis缓存使用 在导入redis依赖后RedisCacheConfiguration类就会自动生效,创建RedisCacheManager,并使用RedisCache进行缓存数据,要缓存的对象的类要实现Serializable接口,默认情况下是以jdk序列化数据 存在redis中,如下:
1 2 3 k:"emp::1" v: \xAC\xED\x00\x05sr\x00$cn.edu.ustc.springboot.bean.Employeeuqf\x03p\x9A\xCF\xE0\x02\x00\x05L\x00\x03dIdt\x00\x13Ljava/lang/Integer;L\x00\x05emailt\x00\x12Ljava/lang/String;L\x00\x06genderq\x00~\x00\x01L\x00\x02idq\x00~\x00\x01L\x00\x08lastNameq\x00~\x00\x02xpsr\x00\x11java.lang.Integer\x12\xE2\xA0\xA4\xF7\x81\x878\x02\x00\x01I\x00\x05valuexr\x00\x10java.lang.Number\x86\xAC\x95\x1D\x0B\x94\xE0\x8B\x02\x00\x00xp\x00\x00\x00\x03t\x00\x07cch@aaasq\x00~\x00\x04\x00\x00\x00\x01q\x00~\x00\x08t\x00\x03cch
要想让对象以json形式 存储在redis中,需要自定义RedisCacheManager,使用GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer类对value进行序列化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 @Configuration public class MyRedisConfig @Bean RedisCacheManager cacheManager (RedisConnectionFactory factory) { RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter = RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(factory); GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer jsonRedisSerializer = new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer(); RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair<Object> serializationPair = RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jsonRedisSerializer); RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfiguration=RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig().serializeValuesWith(serializationPair); RedisCacheManager cacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(cacheWriter,cacheConfiguration); return cacheManager; } }
序列化数据如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 k:"emp::3" v: { "@class" : "cn.edu.ustc.springboot.bean.Employee" , "id" : 3 , "lastName" : "aaa" , "email" : "aaaa" , "gender" : 1 , "dId" : 5 }
注意 ,这里必须用GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer 进行value的序列化解析,如果使用Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer,序列化的json没有"@class": "cn.edu.ustc.springboot.bean.Employee",在读取缓存时会报类型转换异常。
4. Redis缓存原理 配置类RedisCacheConfiguration向容器中导入了其定制的RedisCacheManager,在默认的RedisCacheManager的配置中,是使用jdk序列化value值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 @Configuration (proxyBeanMethods = false )@ConditionalOnClass (RedisConnectionFactory.class ) @AutoConfigureAfter (RedisAutoConfiguration .class ) @ConditionalOnBean (RedisConnectionFactory .class ) @ConditionalOnMissingBean (CacheManager .class ) @Conditional (CacheCondition .class ) class RedisCacheConfiguration @Bean RedisCacheManager cacheManager (CacheProperties cacheProperties, CacheManagerCustomizers cacheManagerCustomizers, ObjectProvider<org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration> redisCacheConfiguration, ObjectProvider<RedisCacheManagerBuilderCustomizer> redisCacheManagerBuilderCustomizers, RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) RedisCacheManagerBuilder builder = RedisCacheManager.builder(redisConnectionFactory).cacheDefaults( determineConfiguration(cacheProperties, redisCacheConfiguration, resourceLoader.getClassLoader())); List<String> cacheNames = cacheProperties.getCacheNames(); if (!cacheNames.isEmpty()) { builder.initialCacheNames(new LinkedHashSet<>(cacheNames)); } redisCacheManagerBuilderCustomizers.orderedStream().forEach((customizer) -> customizer.customize(builder)); return cacheManagerCustomizers.customize(builder.build()); } private org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration determineConfiguration ( CacheProperties cacheProperties, ObjectProvider<org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration> redisCacheConfiguration, ClassLoader classLoader) return redisCacheConfiguration.getIfAvailable(() -> createConfiguration(cacheProperties, classLoader)); } private org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration createConfiguration ( CacheProperties cacheProperties, ClassLoader classLoader) Redis redisProperties = cacheProperties.getRedis(); org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration config = org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration .defaultCacheConfig(); config = config.serializeValuesWith( SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer(classLoader))); if (redisProperties.getTimeToLive() != null ) { config = config.entryTtl(redisProperties.getTimeToLive()); } if (redisProperties.getKeyPrefix() != null ) { config = config.prefixKeysWith(redisProperties.getKeyPrefix()); } if (!redisProperties.isCacheNullValues()) { config = config.disableCachingNullValues(); } if (!redisProperties.isUseKeyPrefix()) { config = config.disableKeyPrefix(); } return config; } }
RedisCacheManager的直接构造类,该类保存了配置类RedisCacheConfiguration,该配置在会传递给RedisCacheManager
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public static class RedisCacheManagerBuilder private final RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter; private RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfiguration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig(); private final Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> initialCaches = new LinkedHashMap<>(); private boolean enableTransactions; boolean allowInFlightCacheCreation = true ; private RedisCacheManagerBuilder (RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter) this .cacheWriter = cacheWriter; } public RedisCacheManagerBuilder cacheDefaults (RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfiguration) Assert.notNull(defaultCacheConfiguration, "DefaultCacheConfiguration must not be null!" ); this .defaultCacheConfiguration = defaultCacheConfiguration; return this ; } public RedisCacheManager build () RedisCacheManager cm = new RedisCacheManager(cacheWriter, defaultCacheConfiguration, initialCaches, allowInFlightCacheCreation); cm.setTransactionAware(enableTransactions); return cm; }
RedisCacheConfiguration保存了许多缓存规则,这些规则都保存在RedisCacheManagerBuilder的RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfiguration属性中,并且当RedisCacheManagerBuilder创建RedisCacheManager传递过去
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public class RedisCacheConfiguration private final Duration ttl; private final boolean cacheNullValues; private final CacheKeyPrefix keyPrefix; private final boolean usePrefix; private final SerializationPair<String> keySerializationPair; private final SerializationPair<Object> valueSerializationPair; private final ConversionService conversionService; public static RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfig (@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) DefaultFormattingConversionService conversionService = new DefaultFormattingConversionService(); registerDefaultConverters(conversionService); return new RedisCacheConfiguration(Duration.ZERO, true , true , CacheKeyPrefix.simple(), SerializationPair.fromSerializer(RedisSerializer.string()), SerializationPair.fromSerializer(RedisSerializer.java(classLoader)), conversionService); }
RedisCacheManager在创建RedisCache时将RedisCacheConfiguration传递过去,并在创建RedisCache时通过createRedisCache()起作用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public class RedisCacheManager extends AbstractTransactionSupportingCacheManager private final RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter; private final RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfig; private final Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> initialCacheConfiguration; private final boolean allowInFlightCacheCreation; protected RedisCache createRedisCache (String name, @Nullable RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfig) return new RedisCache(name, cacheWriter, cacheConfig != null ? cacheConfig : defaultCacheConfig); }
RedisCache,Redis缓存,具体负责将缓存数据序列化的地方,将RedisCacheConfiguration的序列化对SerializationPair提取出来并使用其定义的序列化方式分别对k和v进行序列化操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 public class RedisCache extends AbstractValueAdaptingCache private static final byte [] BINARY_NULL_VALUE = RedisSerializer.java().serialize(NullValue.INSTANCE); private final String name; private final RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter; private final RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfig; private final ConversionService conversionService; public void put (Object key, @Nullable Object value) Object cacheValue = preProcessCacheValue(value); if (!isAllowNullValues() && cacheValue == null ) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format( "Cache '%s' does not allow 'null' values. Avoid storing null via '@Cacheable(unless=\"#result == null\")' or configure RedisCache to allow 'null' via RedisCacheConfiguration." , name)); } cacheWriter.put(name, createAndConvertCacheKey(key), serializeCacheValue(cacheValue), cacheConfig.getTtl()); } protected byte [] serializeCacheKey(String cacheKey) { return ByteUtils.getBytes(cacheConfig.getKeySerializationPair().write(cacheKey)); } protected byte [] serializeCacheValue(Object value) { if (isAllowNullValues() && value instanceof NullValue) { return BINARY_NULL_VALUE; } return ByteUtils.getBytes(cacheConfig.getValueSerializationPair().write(value)); }
分析到这也就不难理解,要使用json保存序列化数据时,需要自定义RedisCacheManager,在RedisCacheConfiguration中定义序列化转化规则,并向RedisCacheManager传入我们自己定制的RedisCacheConfiguration了,我定制的序列化规则会跟随RedisCacheConfiguration一直传递到RedisCache,并在序列化时发挥作用。
延伸 JetCache JSR107介绍 JetCache介绍 Spring Cache框架 SpringBoot-权威教程-雷丰阳