Design Patterns(九) Facade
Facade pattern hides the complexities of the system and provides an interface to the client using which the client can access the system. This type of design pattern comes under structural pattern as this pattern adds an interface to existing system to hide its complexities.This pattern involves a single class which provides simplified methods required by client and delegates calls to methods of existing system classes.
前言 外观模式(Facade Pattern)隐藏系统的复杂性,并向客户端提供了一个客户端可以访问系统的接口。这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式,它向现有的系统添加一个接口,来隐藏系统的复杂性。这种模式涉及到一个单一的类,该类提供了客户端请求的简化方法和对现有系统类方法的委托调用。
外观模式 基本介绍:
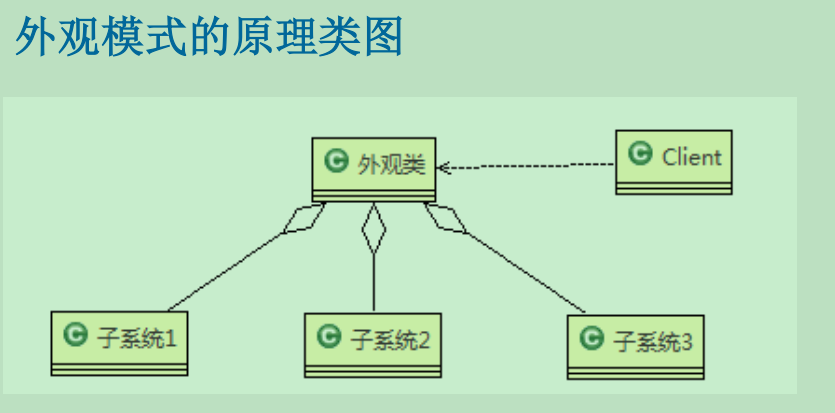
1) 外观模式(Facade),也叫“过程模式:外观模式为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面,此模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用;
2) 外观模式通过定义一个一致的接口,用以屏蔽内部子系统的细节,使得调用端只需跟这个接口发生调用,而无需关心这个子系统的内部细节。
外观模式-UML图:
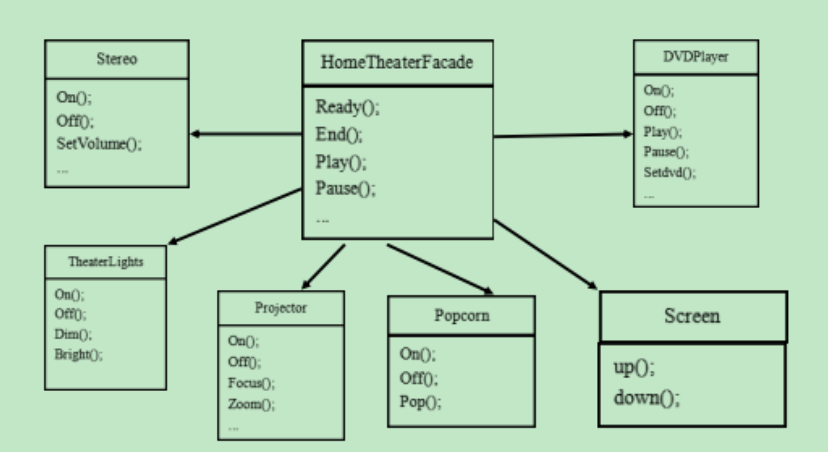
外观模式-案例图:
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 public class Facade DVDPlayer dvdPlayer; Screen screen; Popcorn popcorn; Projector projector; TheaterLights theaterLights; Stereo stereo; public Facade () this .dvdPlayer = DVDPlayer.getInstance(); this .screen = Screen.getInstance(); this .popcorn = Popcorn.getInstance(); this .projector = Projector.getInstance(); this .theaterLights = TheaterLights.getInstance(); this .stereo = Stereo.getInstance(); } public void read () dvdPlayer.on(); screen.down(); popcorn.on(); projector.on(); theaterLights.on(); theaterLights.dim(); stereo.on(); } public void play () dvdPlayer.setDvd(); dvdPlayer.playing(); projector.focus(); stereo.setVolume(); } public void pause () dvdPlayer.pause(); popcorn.pop(); projector.zoom(); } public void end () dvdPlayer.off(); screen.up(); popcorn.off(); projector.off(); theaterLights.bright(); theaterLights.off(); stereo.off(); } public static void main (String[] args) Facade facade = new Facade(); facade.read(); facade.play(); facade.pause(); facade.end(); } } class DVDPlayer private final static DVDPlayer dvdPlayer = new DVDPlayer(); private DVDPlayer () } public static DVDPlayer getInstance () return dvdPlayer; } public void on () System.out.println("DVDPlayer is On" ); } public void off () System.out.println("DVDPlayer is Off" ); } public void setDvd () System.out.println("DVDPlayer is Setting" ); } public void playing () System.out.println("DVDPlayer is Playing" ); } public void pause () System.out.println("DVDPlayer is Pause" ); } } class Screen private final static Screen screen = new Screen(); private Screen () } public static Screen getInstance () return screen; } public void up () System.out.println("Screen is up" ); } public void down () System.out.println("Screen is down" ); } } class Popcorn private final static Popcorn popcorn = new Popcorn(); private Popcorn () } public static Popcorn getInstance () return popcorn; } public void on () System.out.println("Popcorn is on" ); } public void off () System.out.println("Popcorn is off" ); } public void pop () System.out.println("Popcorn is pop" ); } } class Projector private final static Projector projector = new Projector(); private Projector () } public static Projector getInstance () return projector; } public void on () System.out.println("Projector is on" ); } public void off () System.out.println("Projector is off" ); } public void focus () System.out.println("Projector is focus" ); } public void zoom () System.out.println("Projector is zoom" ); } } class TheaterLights private final static TheaterLights theaterLights = new TheaterLights(); private TheaterLights () } public static TheaterLights getInstance () return theaterLights; } public void on () System.out.println("TheaterLights is on" ); } public void off () System.out.println("TheaterLights is off" ); } public void dim () System.out.println("TheaterLights is dim" ); } public void bright () System.out.println("TheaterLights is bright" ); } } class Stereo private final static Stereo stereo = new Stereo(); private Stereo () } public static Stereo getInstance () return stereo; } public void on () System.out.println("Stereo is on" ); } public void off () System.out.println("Stereo is off" ); } public void setVolume () System.out.println("Stereo is setVolume" ); } }
总结 组合模式的注意事项和细节:
1) 外观模式对外屏蔽了子系统的细节,因此外观模式降低了客户端对子系统使用的复杂性;
延伸 外观模式 外观模式-菜鸟教程 外观模式(Facade模式)详解 Design Patterns - Facade Pattern 尚硅谷Java设计模式,韩顺平图解java设计模式
<
Design Patterns(十) Flyweight
Algorithm Sort Introduction
>