Design Patterns(十五) Iterator
Iterator pattern is very commonly used design pattern in Java and .Net programming environment. This pattern is used to get a way to access the elements of a collection object in sequential manner without any need to know its underlying representation.
前言 迭代器模式(Iterator),提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中的各种元素,而又不暴露该对象的内部表示。
迭代器模式 基本介绍:
1) 迭代器模式(Iterator Pattern)是常用的设计模式,属于行为型模式;
角色介绍:
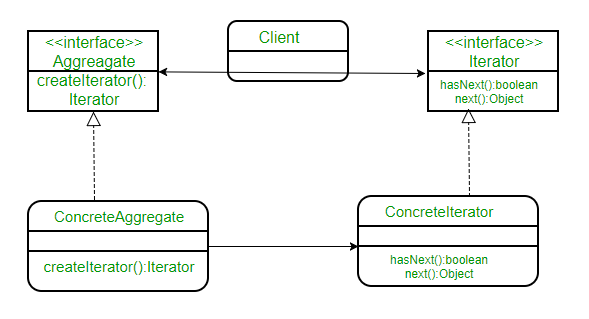
1)Iterator(迭代器)迭代器定义访问和遍历元素的接口;
迭代器模式-UML图:
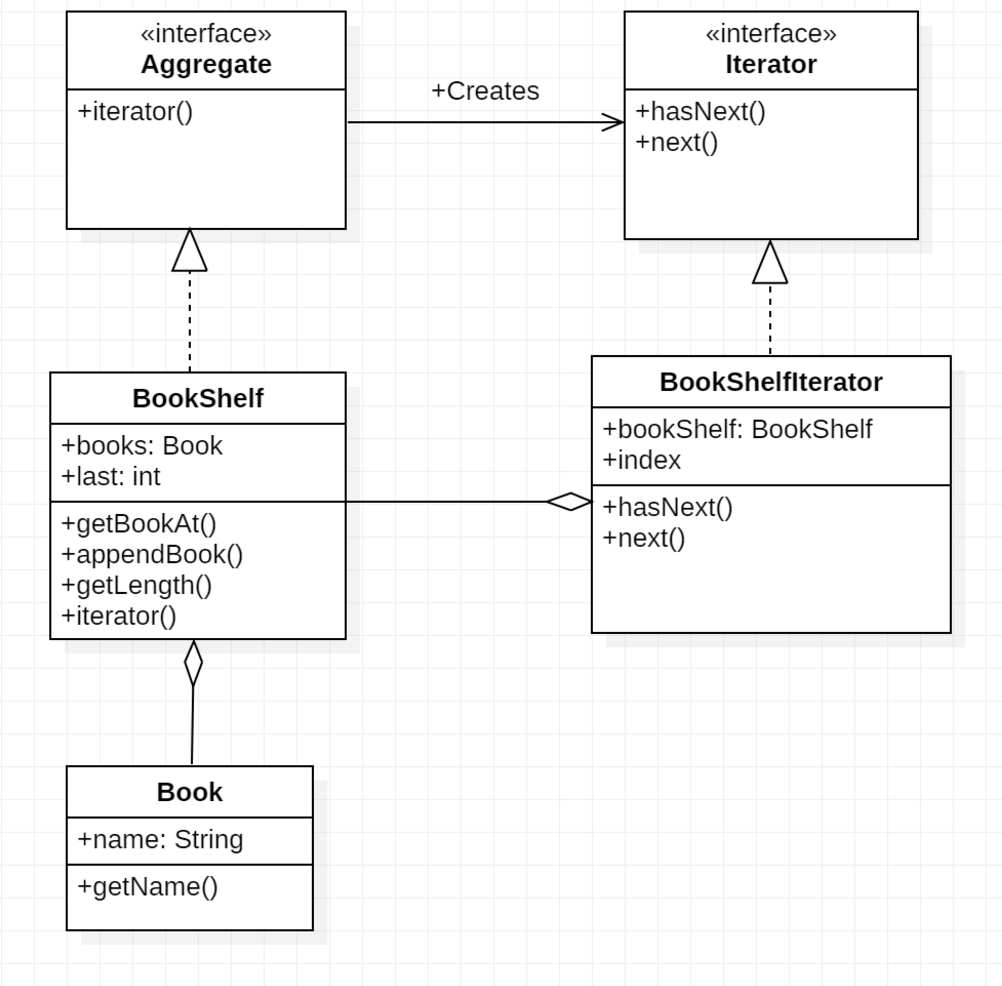
迭代器模式-实例图:
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;public class IteratorDemo public static void main (String[] args) BookShelf bookShelf = new BookShelf(); bookShelf.appendBook(new Book("Around the World in 80 Days" )); bookShelf.appendBook(new Book("Bible" )); bookShelf.appendBook(new Book("Cinderella" )); bookShelf.appendBook(new Book("Daddy-Long-Legs" )); Iterator it = bookShelf.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { Book book = (Book) it.next(); System.out.println(book.getName()); } } } interface Aggregate public abstract Iterator iterator () } interface Iterator public abstract boolean hasNext () public abstract Object next () } class Book private String name; public Book (String name) this .name = name; } public String getName () return name; } } class BookShelf implements Aggregate private List<Book> books; public BookShelf () this .books = new ArrayList<Book>(); } public Book getBookAt (int index) return books.get(index); } public void appendBook (Book book) books.add(book); } public int getLength () return books.size(); } public Iterator iterator () return new BookShelfIterator(this ); } } class BookShelfIterator implements Iterator private BookShelf bookShelf; private int index; public BookShelfIterator (BookShelf bookShelf) this .bookShelf = bookShelf; this .index = 0 ; } public boolean hasNext () if (index < bookShelf.getLength()) { return true ; } else { return false ; } } public Object next () Book book = bookShelf.getBookAt(index); index++; return book; } }
总结 迭代器模式的注意事项和细节:
优 点
1) 提供一个统一的方法遍历对象,客户不用再考虑聚合的类型,使用一种方法就可以遍历对象了;
缺 点
延伸 迭代器模式 迭代器模式-菜鸟教程 迭代器模式简析 Design Patterns - Iterator Pattern 尚硅谷Java设计模式,韩顺平图解java设计模式
<
Design Patterns(十六) Observer
Design Patterns(十四) Visitor
>