A graph is a pictorial representation of a set of objects where some pairs of objects are connected by links. The interconnected objects are represented by points termed as vertices, and the links that connect the vertices are called edges.
前言 在计算机科学中,一个图就是一些顶点的集合,这些顶点通过一系列边结对(连接)。顶点用圆圈表示,边就是这些圆圈之间的连线。顶点之间通过边连接。
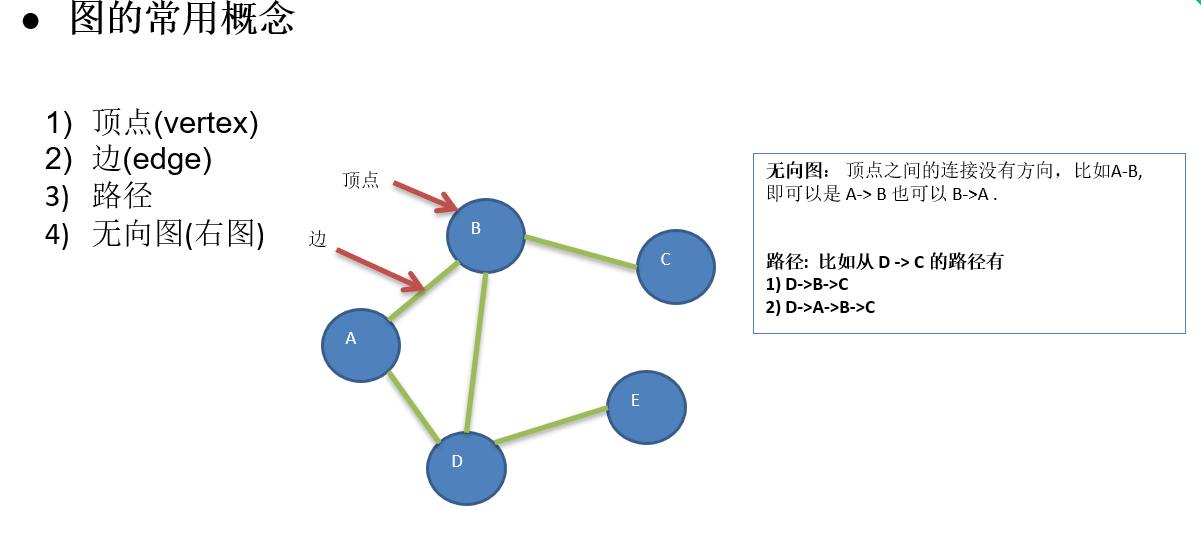
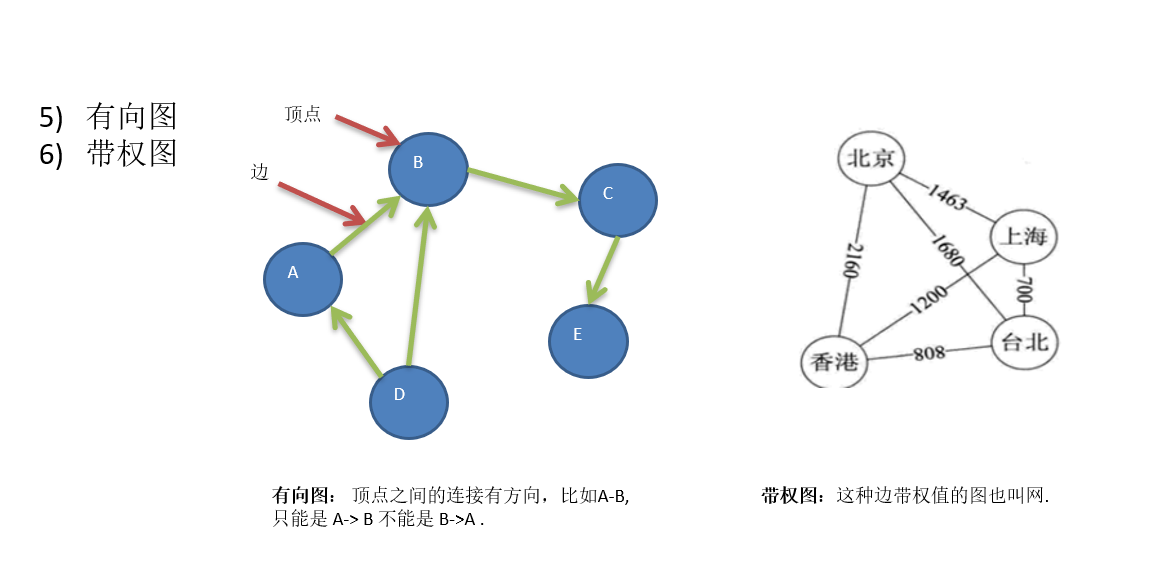
图 图的介绍: 图是由顶点的有穷非空集合和顶点之间边的集合组成, 通常表示为: G(V,E), 其中,G表示一个图,V是图G中顶点的集合,E是图G中边的集合。
图解:
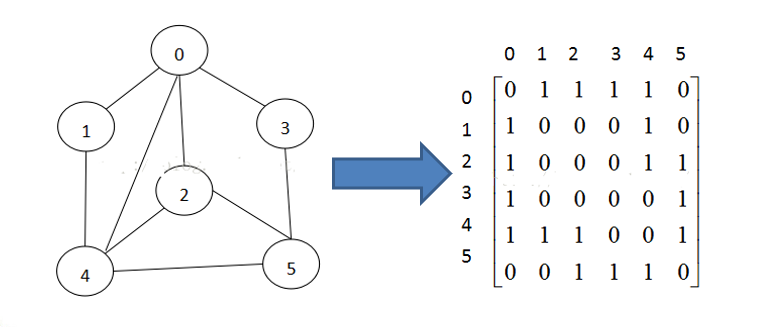
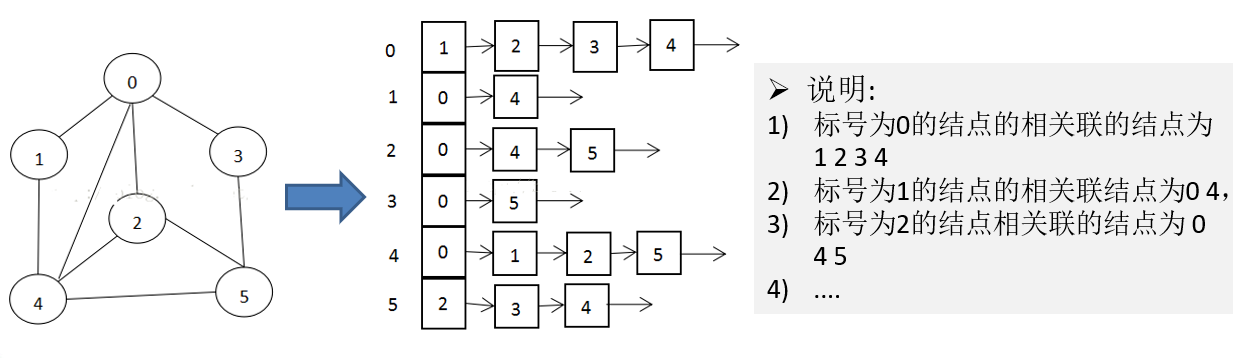
图的表示方式: 图的表示方式有两种:二维数组表示(邻接矩阵);链表表示(邻接表)。
2)邻接表
图的访问策略: 1)深度优先遍历
图的深度优先搜索(Depth First Search) 。
深度优先遍历算法步骤
2)广度优先遍历
图的广度优先搜索(Broad First Search) 。
广度优先遍历算法步骤
图代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.LinkedList;import java.util.List;public class Graph private List<String> vertexs; private int [][] edges; private int numOfEdge; private boolean [] isVisited; public static void main (String[] args) Graph graph = new Graph(5 ); String[] vertexStr = {"A" , "B" , "C" , "D" , "E" }; for (String vertex : vertexStr) { graph.insertVertex(vertex); } graph.insertEdge(0 , 1 , 1 ); graph.insertEdge(0 , 2 , 1 ); graph.insertEdge(1 , 2 , 1 ); graph.insertEdge(1 , 3 , 1 ); graph.insertEdge(1 , 4 , 1 ); graph.showGraph(); System.out.println("深度遍历" ); graph.dfs(); System.out.println(); System.out.println("广度优先!" ); graph.bfs(); } public Graph (int vertexNum) vertexs = new ArrayList<>(vertexNum); edges = new int [vertexNum][vertexNum]; numOfEdge = 0 ; } public void insertVertex (String vertex) vertexs.add(vertex); } public void insertEdge (int index1, int index2, int weight) edges[index1][index2] = weight; edges[index2][index1] = weight; numOfEdge++; } public int getNumOfVertex () return vertexs.size(); } public int getNumOfEdge () return numOfEdge; } public String getVertexValueByIndex (int index) return vertexs.get(index); } public int getWeight (int index1, int index2) return edges[index1][index2]; } public void showGraph () for (int [] link : edges) { System.out.println(Arrays.toString(link)); } } public int getFirstNeighbor (int index) for (int j = 0 ; j < vertexs.size(); j++) { if (edges[index][j] > 0 ) { return j; } } return -1 ; } public int getNextNeighbor (int v1, int v2) for (int j = v2 + 1 ; j < vertexs.size(); j++) { if (edges[v1][j] > 0 ) { return j; } } return -1 ; } private void dfs (boolean [] isVisited, int i) System.out.print(getVertexValueByIndex(i) + "->" ); isVisited[i] = true ; int w = getFirstNeighbor(i); while (w != -1 ) { if (!isVisited[w]) { dfs(isVisited, w); } w = getNextNeighbor(i, w); } } public void dfs () isVisited = new boolean [vertexs.size()]; for (int i = 0 ; i < getNumOfVertex(); i++) { if (!isVisited[i]) { dfs(isVisited, i); } } } private void bfs (boolean [] isVisited, int i) int u ; int w ; LinkedList queue = new LinkedList(); System.out.print(getVertexValueByIndex(i) + "=>" ); isVisited[i] = true ; queue.addLast(i); while ( !queue.isEmpty()) { u = (Integer)queue.removeFirst(); w = getFirstNeighbor(u); while (w != -1 ) { if (!isVisited[w]) { System.out.print(getVertexValueByIndex(w) + "=>" ); isVisited[w] = true ; queue.addLast(w); } w = getNextNeighbor(u, w); } } } public void bfs () isVisited = new boolean [vertexs.size()]; for (int i = 0 ; i < getNumOfVertex(); i++) { if (!isVisited[i]) { bfs(isVisited, i); } } } }
延伸 图-百度百科 数据结构——图 数据结构:图(Graph) 韩顺平数据结构和算法 Data Structure - Graph