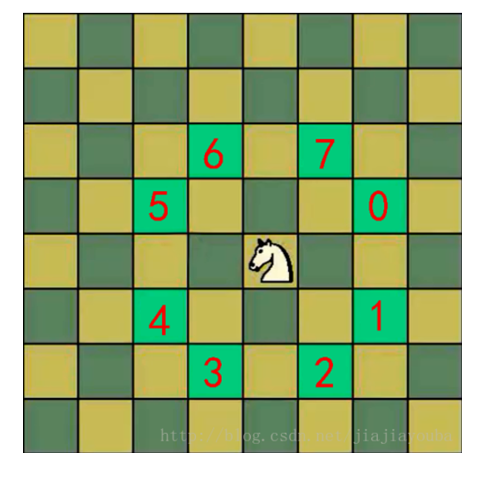
Knight’s tour is a sequence of moves of a knight on a chessboard such that the knight visits every square exactly once. If the knight ends on a square that is one knight’s move from the beginning square (so that it could tour the board again immediately, following the same path), the tour is closed; otherwise, it is open.
前言 马踏棋盘是经典的程序设计问题之一,主要的解决方案有两种:一种是基于深度优先搜索的方法,另一种是基于贪婪算法的方法。第一种基于深度优先搜索的方法是比较常用的算法,深度优先搜索算法也是数据结构中的经典算法之一,主要是采用递归的思想,一级一级的寻找,遍历出所有的结果,最后找到合适的解。而基于贪婪的算法则是制定贪心准则,一旦设定不能修改,他只关心局部最优解,但不一定能得到最优解。
马踏棋盘算法 马踏棋盘算法介绍:
1)马踏棋盘算法也被称为骑士周游问题;
马踏棋盘算法步骤:
1)马踏棋盘问题(骑士周游问题)实际上是图的深度优先搜索(DFS)的应用;
马踏棋盘算法问题:
马踏棋盘算法代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 import java.awt.Point;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Comparator;public class KnightTour private static int X; private static int Y; private static boolean visited[]; private static boolean finished; public static void main (String[] args) System.out.println("骑士周游算法,开始运行~~" ); X = 8 ; Y = 8 ; int row = 1 ; int column = 1 ; int [][] chessboard = new int [X][Y]; visited = new boolean [X * Y]; long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); traversalChessboard(chessboard, row - 1 , column - 1 , 1 ); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("共耗时: " + (end - start) + " 毫秒" ); for (int [] rows : chessboard) { for (int step : rows) { System.out.print(step + "\t" ); } System.out.println(); } } public static void traversalChessboard (int [][] chessboard, int row, int column, int step) chessboard[row][column] = step; visited[row * X + column] = true ; ArrayList<Point> ps = next(new Point(column, row)); sort(ps); while (!ps.isEmpty()) { Point p = ps.remove(0 ); if (!visited[p.y * X + p.x]) { traversalChessboard(chessboard, p.y, p.x, step + 1 ); } } if (step < X * Y && !finished) { chessboard[row][column] = 0 ; visited[row * X + column] = false ; } else { finished = true ; } } public static ArrayList<Point> next (Point curPoint) ArrayList<Point> ps = new ArrayList<Point>(); Point p1 = new Point(); if ((p1.x = curPoint.x - 2 ) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 1 ) >= 0 ) { ps.add(new Point(p1)); } if ((p1.x = curPoint.x - 1 ) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 2 ) >= 0 ) { ps.add(new Point(p1)); } if ((p1.x = curPoint.x + 1 ) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 2 ) >= 0 ) { ps.add(new Point(p1)); } if ((p1.x = curPoint.x + 2 ) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y - 1 ) >= 0 ) { ps.add(new Point(p1)); } if ((p1.x = curPoint.x + 2 ) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 1 ) < Y) { ps.add(new Point(p1)); } if ((p1.x = curPoint.x + 1 ) < X && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 2 ) < Y) { ps.add(new Point(p1)); } if ((p1.x = curPoint.x - 1 ) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 2 ) < Y) { ps.add(new Point(p1)); } if ((p1.x = curPoint.x - 2 ) >= 0 && (p1.y = curPoint.y + 1 ) < Y) { ps.add(new Point(p1)); } return ps; } public static void sort (ArrayList<Point> ps) ps.sort(new Comparator<Point>() { @Override public int compare (Point o1, Point o2) int count1 = next(o1).size(); int count2 = next(o2).size(); if (count1 < count2) { return -1 ; } else if (count1 == count2) { return 0 ; } else { return 1 ; } } }); } }
延伸 马踏棋盘的实现 马踏棋盘-百度百科 马踏棋盘(贪心算法) 韩顺平数据结构和算法 Knight’s tour - Wikipedia
<
Netty
Algorithm Floyd
>